Auditory brainstem implants
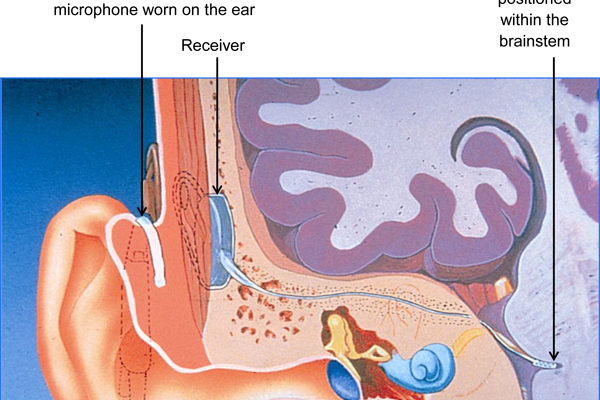
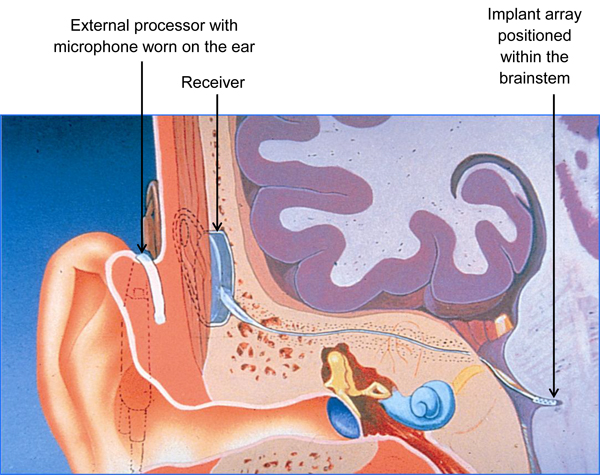
Auditory Brainstem Implants (ABI) are suitable for those with a profound sensorineural hearing loss, leading to near total loss of sound.
This device has two parts: an external part (the ‘processor’, worn on the ear) and the surgically-implanted internal part.
A microphone on the processor picks up the sound around it, and turns it from a sound wave into an electrical signal.
The processor then transmits the sound signal to the internal part of the hearing implant. This consists of a receiver just below the skin, together with the implant array which is positioned within the brainstem.
This means that the implant is bypassing both the cochlea and the hearing nerve, taking a short cut to the brainstem. In this way, the device aims to give a sense of sound when the hearing nerve is not working.
Image: Courtesy of Cochlear Europe.
Who can be considered for an ABI?
One main use of an ABI is for those with the genetic condition called Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2).
If you have NF2, you are likely to have a tumour on or near the hearing nerve. If this tumour is removed for medical reasons, the surgeons may well have to cut across the nerve of hearing. This brings about a complete breakdown of natural hearing in that ear. During the tumour removal surgery, the surgeon may consider placing an this type of implant as an alternative method of hearing.
Other uses of the ABI are for people who are born with no functioning nerve of hearing in either ear, or people who are deaf because of an unusually shaped cochlea. Sometimes meningitis leads to deafness but leaves the cochlea too damaged to take a cochlear implant. However, an ABI for one of these reasons is very rare, because it requires neurosurgery.
What are the likely benefits of an ABI?
An ABI may provide a link to sounds when there would otherwise be no natural hearing at all. It may also help with lipreading.
Any drawbacks of an ABI?
An ABI involves complex neurosurgery to the brainstem. Your consultant would need to discuss all the risks with you.
The results of this implant are extremely variable. It is a difficult task to position the ABI on the brainstem exactly to deliver sound. It is possible that there is no hearing sensation at all from the auditory brainstem implant.
In some cases the hearing sensation is within a narrow range so that sounds are not well differentiated. It takes time to adjust to the sound perceived through an ABI.
For further information on Neurofibromatosis Type 2 please contact:
- The Neuro Foundation.
- Can You Hear Us? is a website for giving a voice to people with Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) and to encourage people to take advantage of adversity.
- Addenbrooke’s Hospital NF2 services website.
Webpage updated: April 2024